People Who Are Heterozygous For Sickle Cell Disease Are Generally Healthy Because They
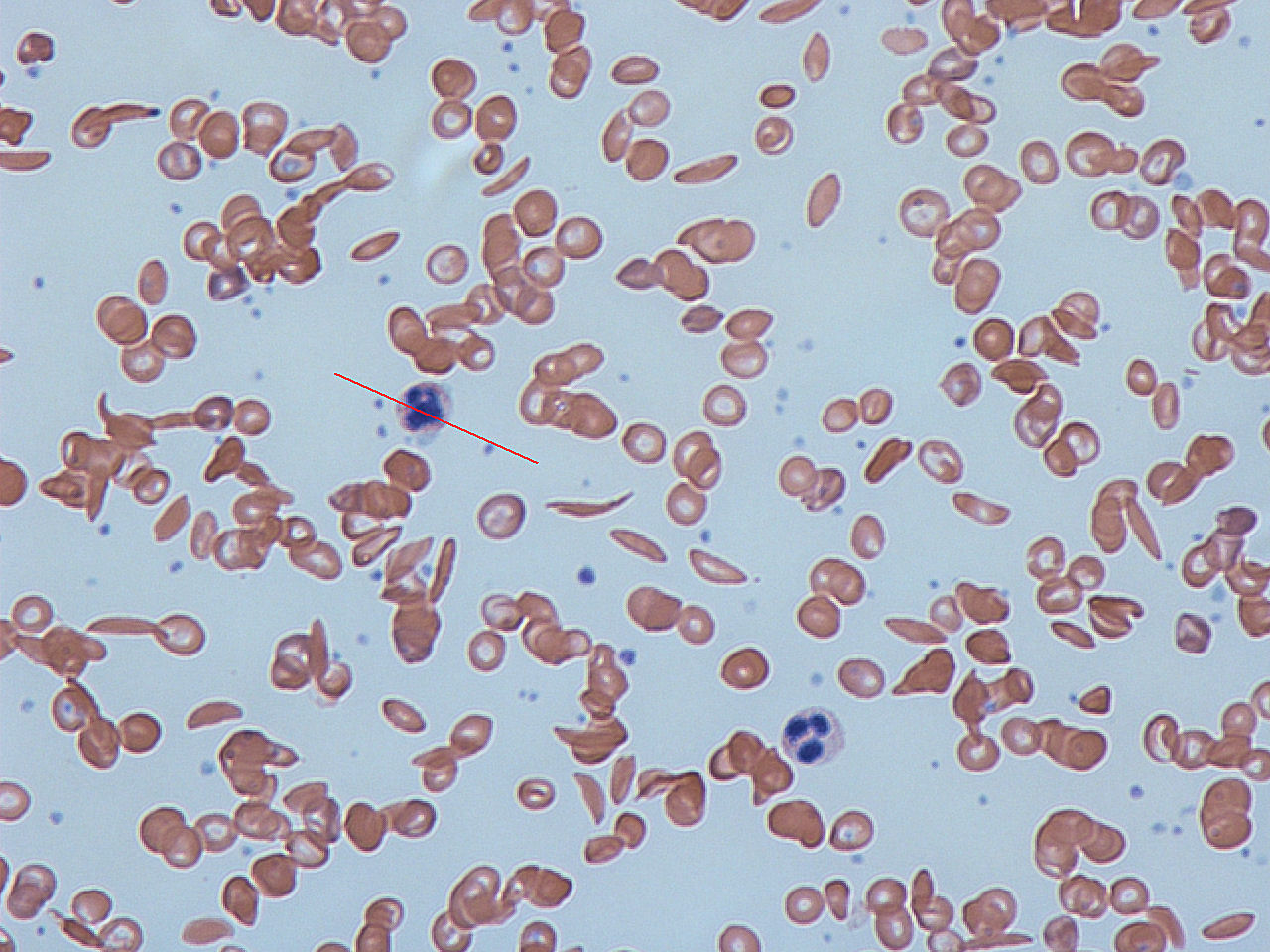
People who are heterozygous for sickle cell disease are generally healthy because they. Signs include headache seizures weakness in the arms and legs speech problems a facial droop or loss of consciousness. Normal red blood cells top and sickle cells bottom They may be maintained by heterozygote advantage When carrying two copies of an allele is disadvantageous but carrying only one copy is advantageous natural selection will not remove the allele from the population the advantage conferred in its heterozygous state keeps the allele around. People who are heterozygous for sickle cell disease are generally healthy because they Nondisjunction The failure of homologous chromosomes to separate properly during meiosis.
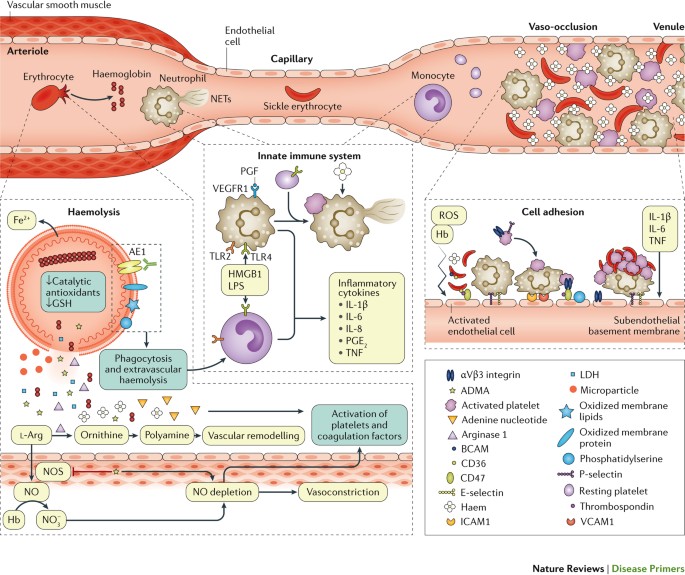
Individuals suffering from sickle cell anemia are frequently ill and generally have a considerably reduced lifespan. Others are less fortunate and can suffer from a variety of complications. People with sickle cell trait are generally asymptomatic and have no abnormal physical findings.
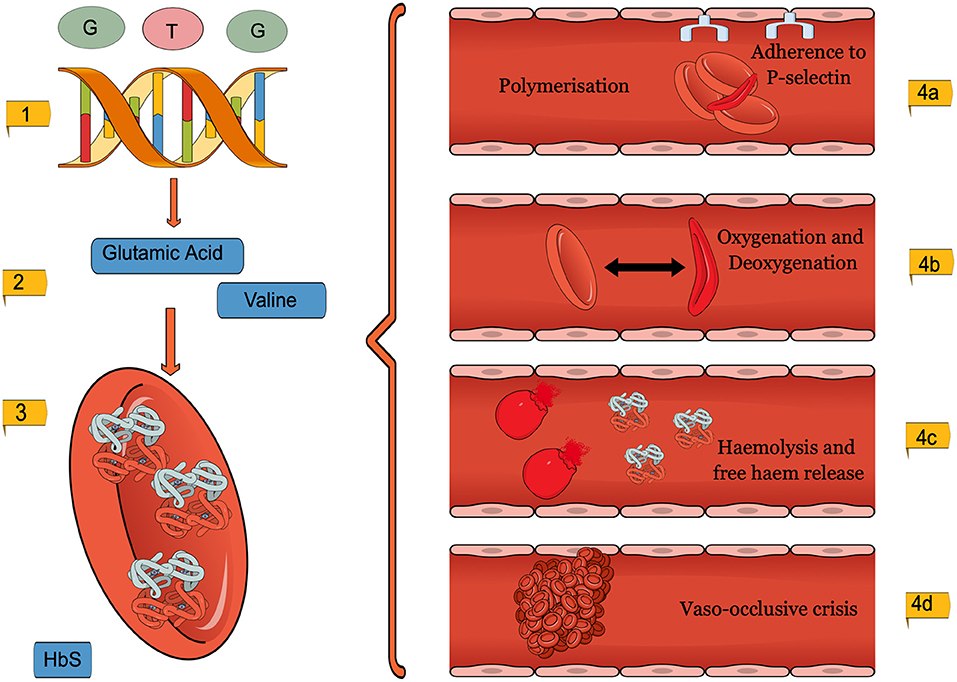
Falciparum malaria has been a leading cause of death in Africa since remote times the sickle cell trait is now more frequently found in Africa and in persons of African ancestry. Cystic fibrosis like sickle cell anaemia occurs when a. People who have sickle cell disease inherit two abnormal hemoglobin genes one from each parent.
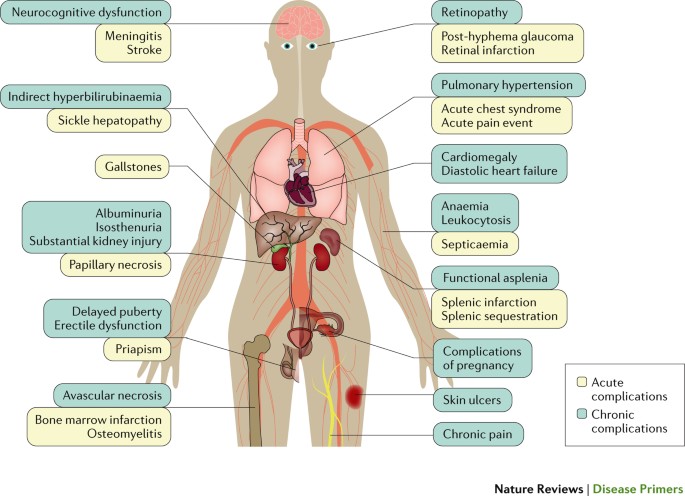
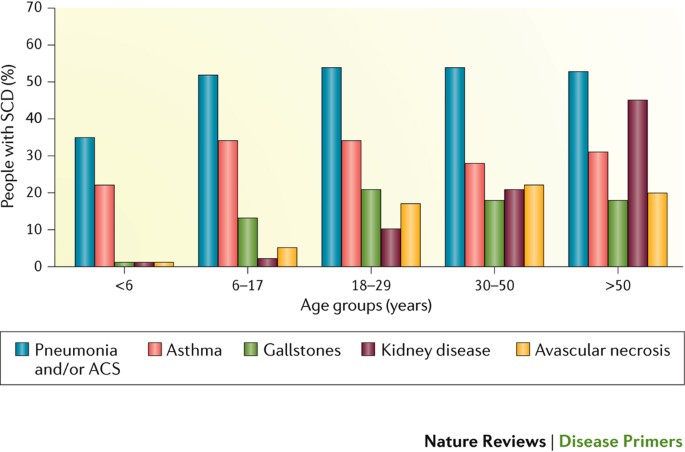
Falciparum infection 2 4. Some people with sickle cell disease lead lives that are nearly normal. People with sickle cell disease are also at risk for problems such as leg ulcers bone or joint damage gallstones kidney damage eye damage and delayed growth.
These individuals make both the usual adult hemoglobin and sickle hemoglobin in roughly equal proportions so they do not experience any health problems as a result of having the trait. Healthy people who have inherited only one mutant gene from one parent of thalassaemia than of sickle-cell anaemia but the high frequency of the sickle-cell gene in certain areas leads to a high rate of affected newborns. Sickle cell trait produces no symptoms or problems for most people.
However sickle cell trait is occasionally associated with significant morbidity - eg haematuria decreased ability to concentrate urine renal papillary necrosis splenic infarction exertional rhabdomyolysis and exercise-related sudden death. The severity of sickle cell disease varies tremendously. Heterozygous with a condition such as hemoglobin AS HbAS.
Falciparum malaria and thus enjoy a biologic advantage. Persons who have the sickle cell trait heterozygotes for the abnormal hemoglobin gene HbS are relatively protected against P.
These individuals are said to have sickle cell disease.
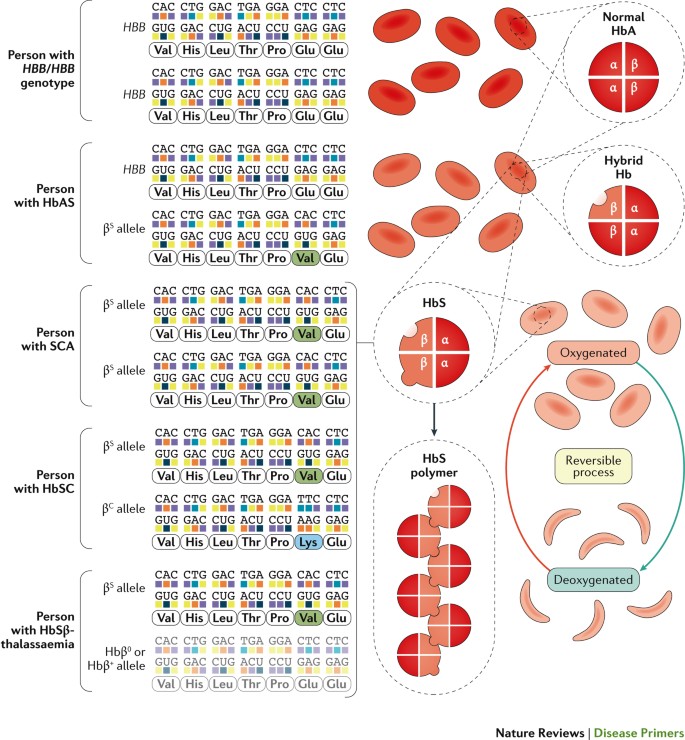
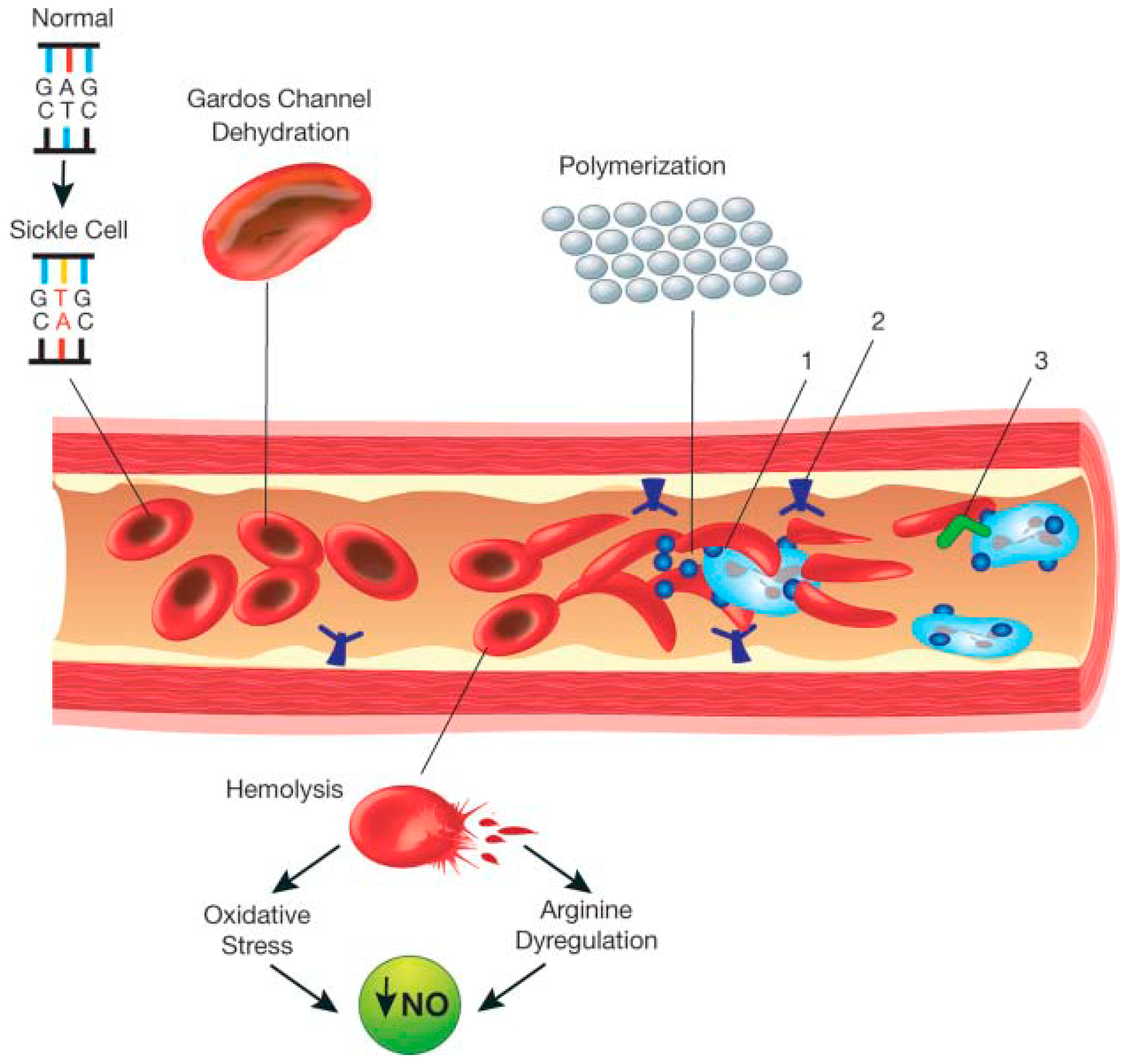
These individuals are said to have sickle cell disease. People with sickle cell disease are also at risk for problems such as leg ulcers bone or joint damage gallstones kidney damage eye damage and delayed growth. When two people who are carriers of an autosomal recessive condition have a child there is a 25 1 in 4 chance that the child will have the condition a 50 1 in 2 chance that the child will be a carrier like each of the parents and a 25 1. Persons who have the sickle cell trait heterozygotes for the abnormal hemoglobin gene HbS are relatively protected against P. People who have sickle cell disease have abnormal hemoglobin called hemoglobin S or sickle hemoglobin in their red blood cells. Signs include headache seizures weakness in the arms and legs speech problems a facial droop or loss of consciousness. Globally there are more carriers ie. Falciparum malaria has been a leading cause of death in Africa since remote times the sickle cell trait is now more frequently found in Africa and in persons of African ancestry. These patients inherited a copy of the variant gene from one parent and may be referred to as carriers or as having the sickle cell trait These patients are usually asymptomatic.
People with sickle cell trait would have a better chance of surviving an outbreak of malaria and passing their genes for sickle and normal hemoglobin to the next generation when they have children. Persons who have the sickle cell trait heterozygotes for the abnormal hemoglobin gene HbS are relatively protected against P. The severity of sickle cell disease varies tremendously. Sickle-cell anaemia is particularly common among people whose ancestors come from. In regards to sickle cell anemia a person who carries one copy of the mutated gene is said to be a carrier for the condition or to have sickle cell trait. People with sickle cell trait would have a better chance of surviving an outbreak of malaria and passing their genes for sickle and normal hemoglobin to the next generation when they have children. Normal red blood cells top and sickle cells bottom They may be maintained by heterozygote advantage When carrying two copies of an allele is disadvantageous but carrying only one copy is advantageous natural selection will not remove the allele from the population the advantage conferred in its heterozygous state keeps the allele around.















/GettyImages-680800893-5a43ffb2494ec9003693de95.jpg)










Post a Comment for "People Who Are Heterozygous For Sickle Cell Disease Are Generally Healthy Because They"