Huntington Disease Cag Repeat
Huntington disease cag repeat. A review and validation study of statistical approaches. The polymorphic CAG repeat that is expanded on Huntington disease HD chromosomes is flanked by a CCG repeat. Mutant HTT mHTT disrupts.
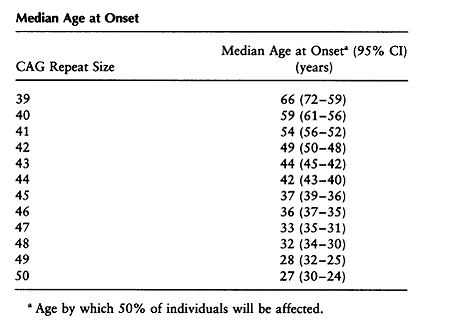
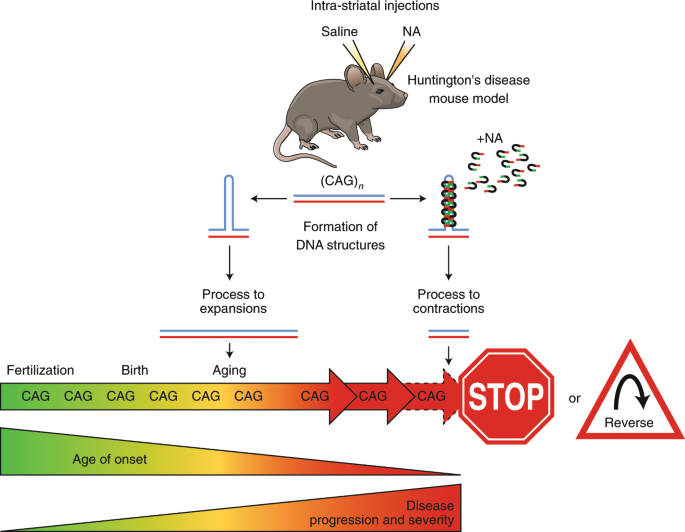
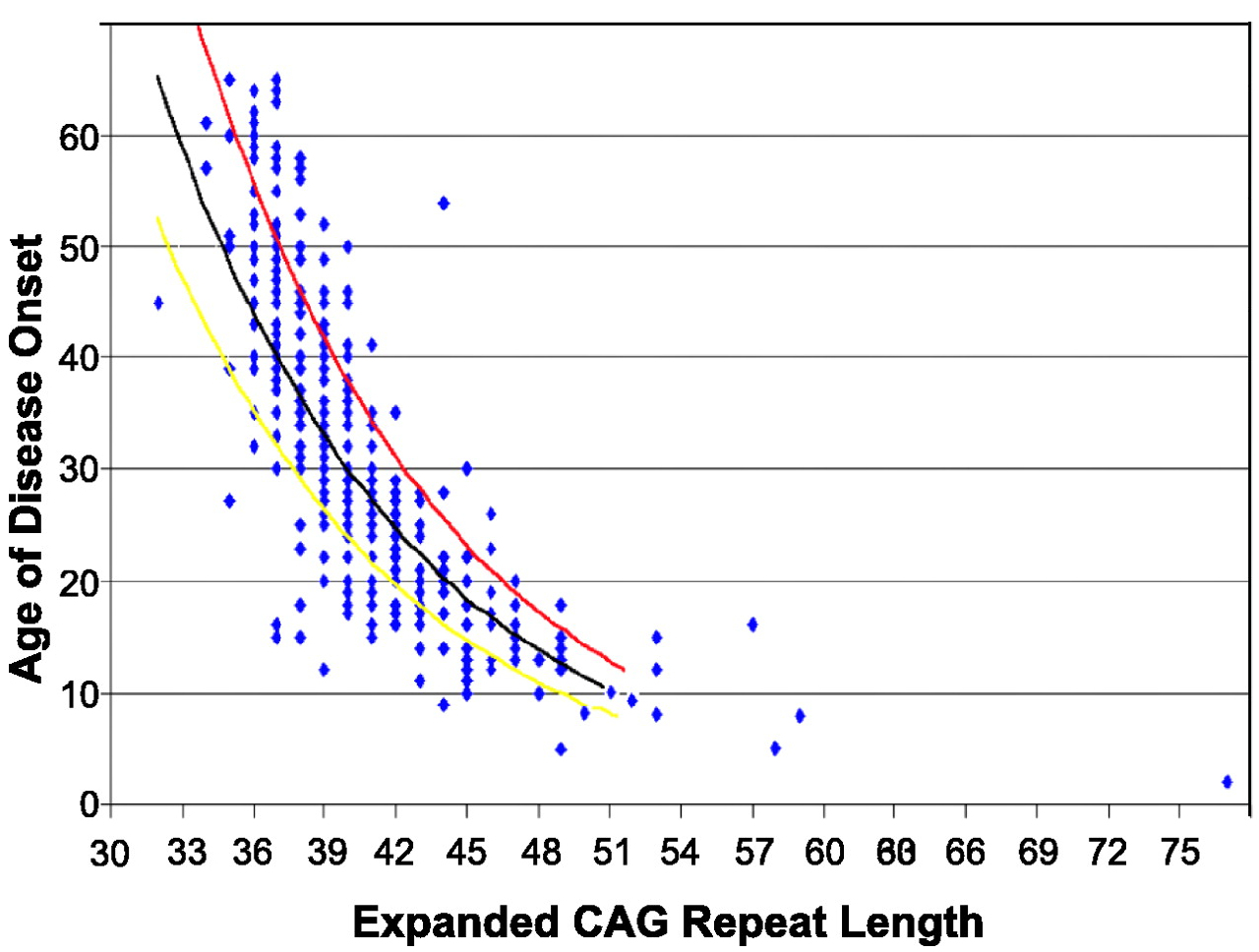
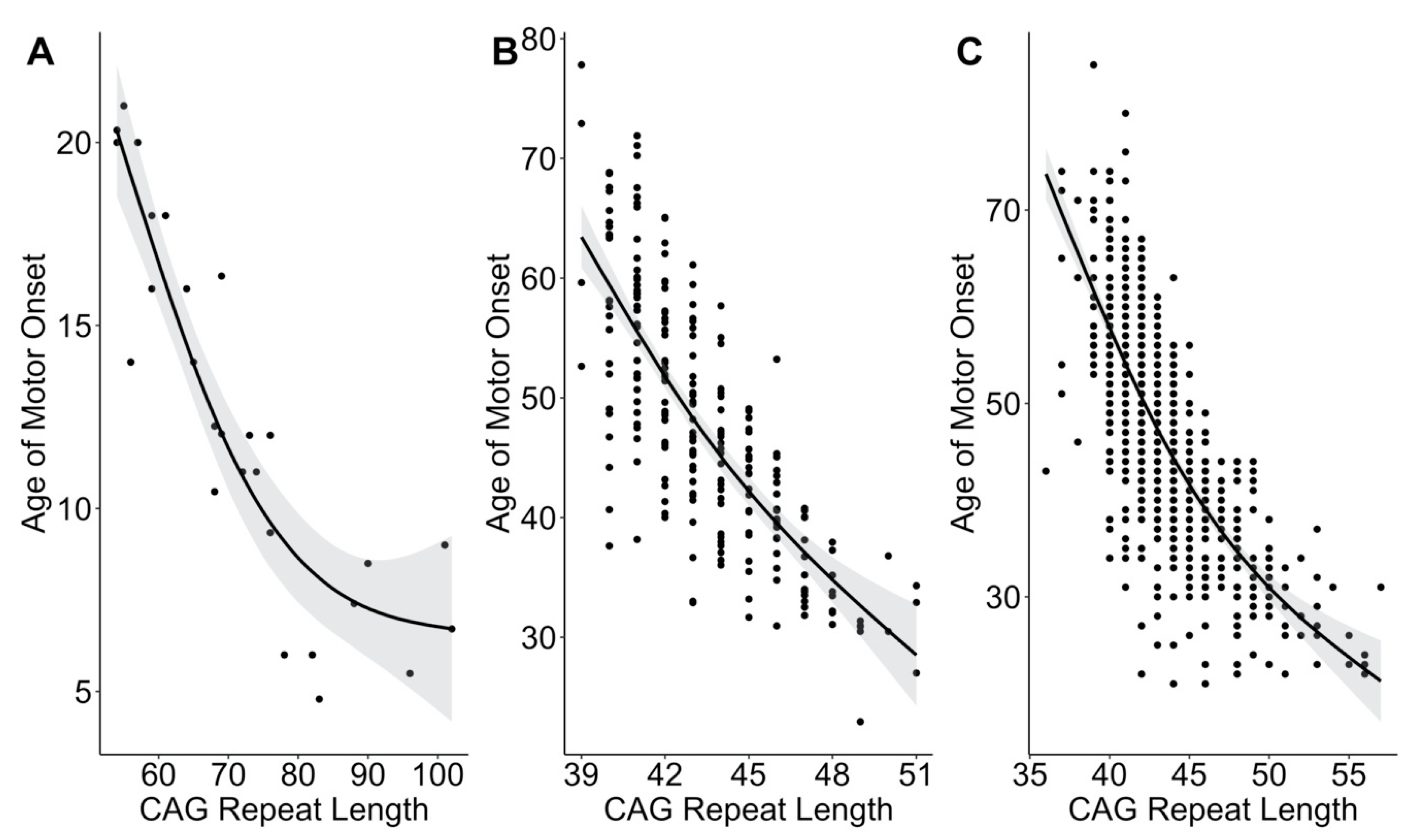
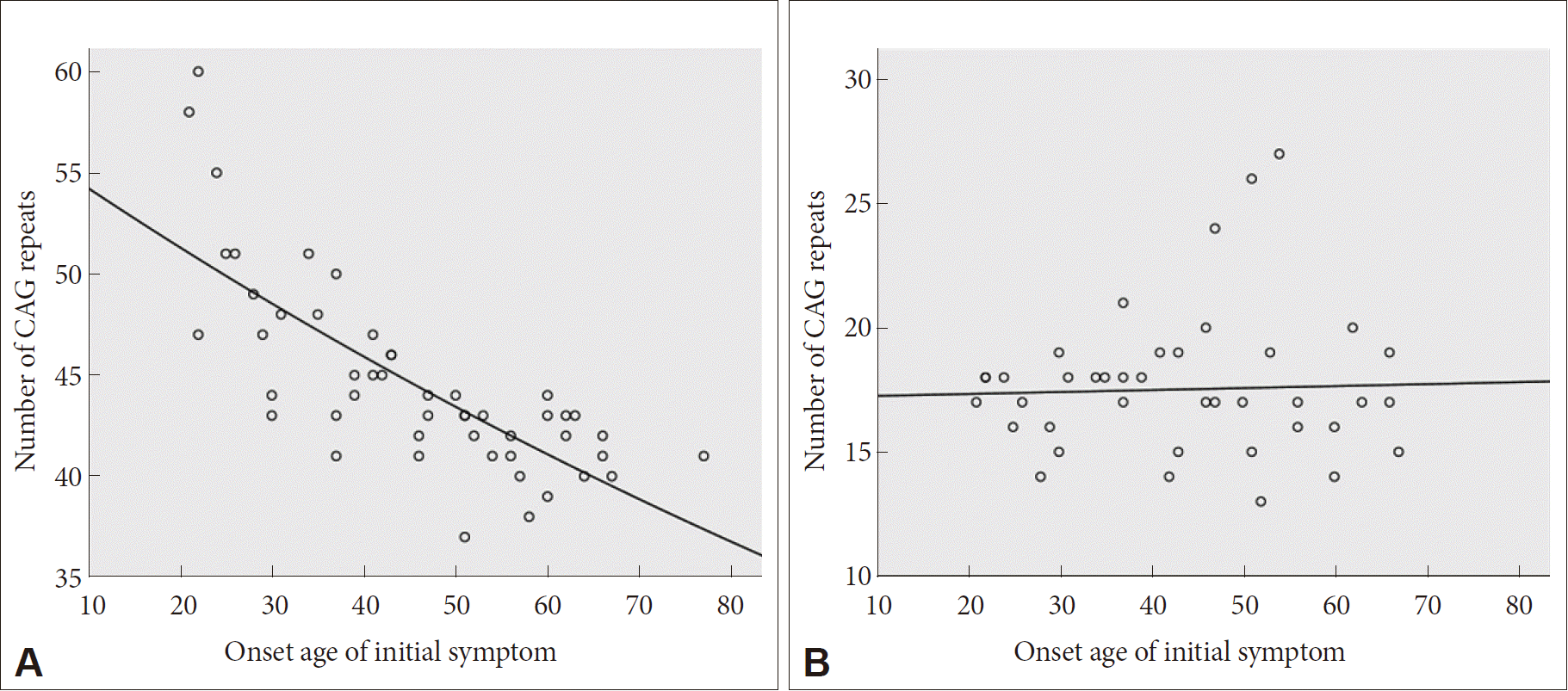
A-E The CAG repeat length associated with each prediction curve is indicated at the upper right of the curve. Longer repeat sequences cause disease onset at a younger age. Here we show that this CCG tract previously assumed to be invariant at seven CCG repeats is.
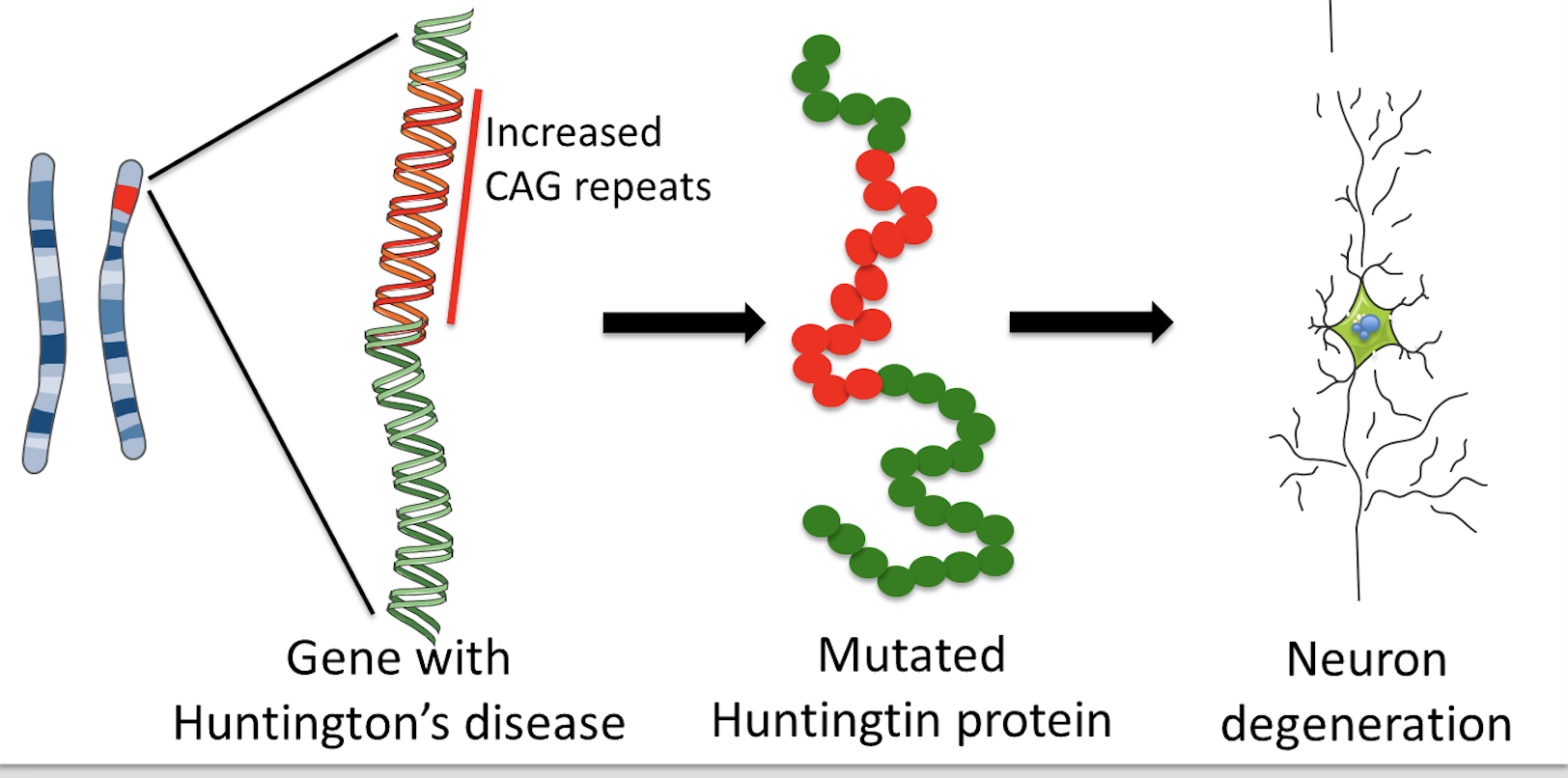
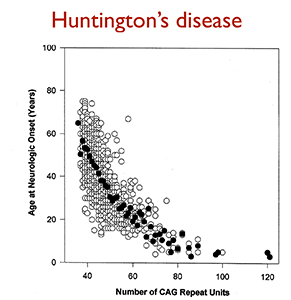
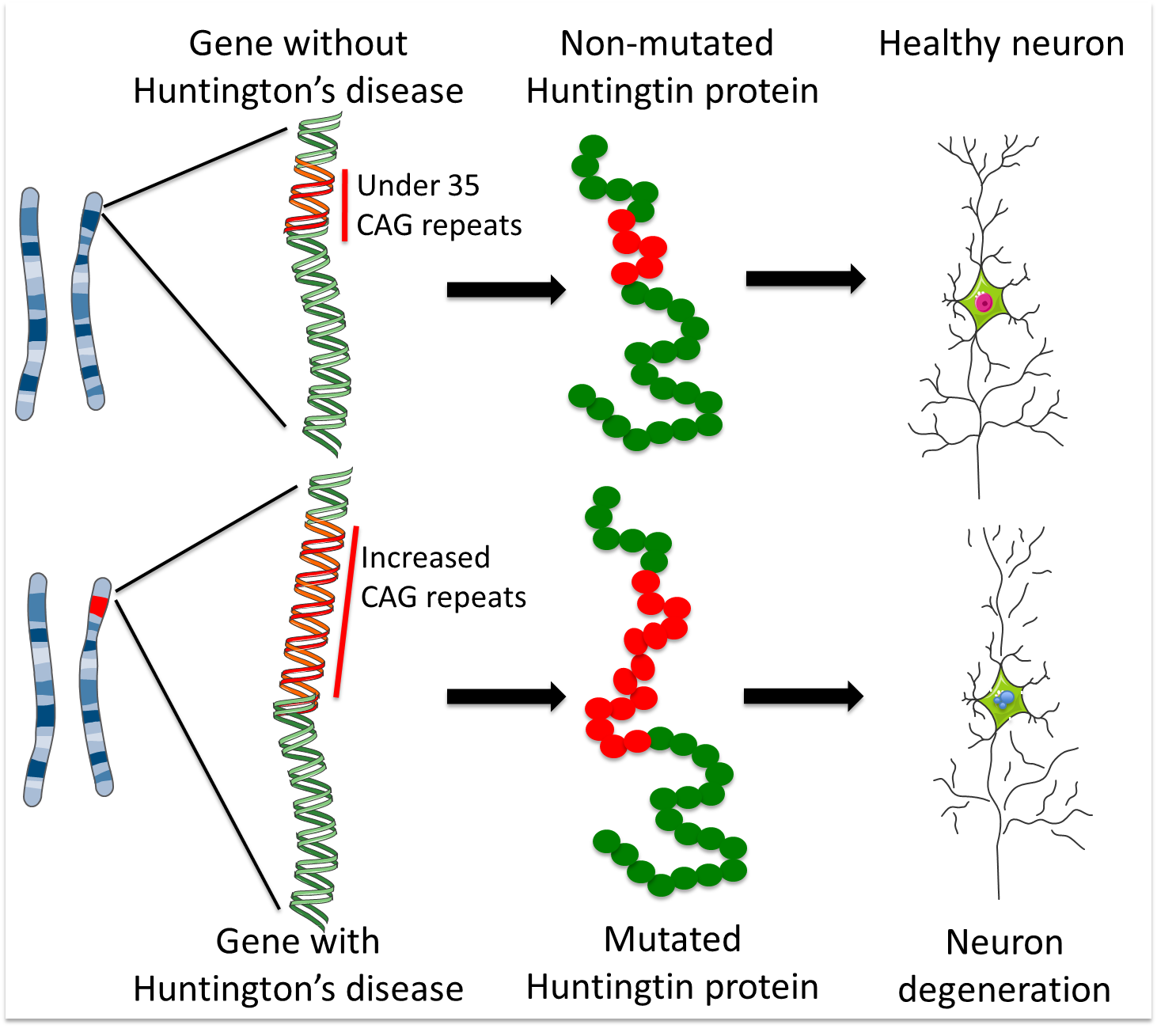
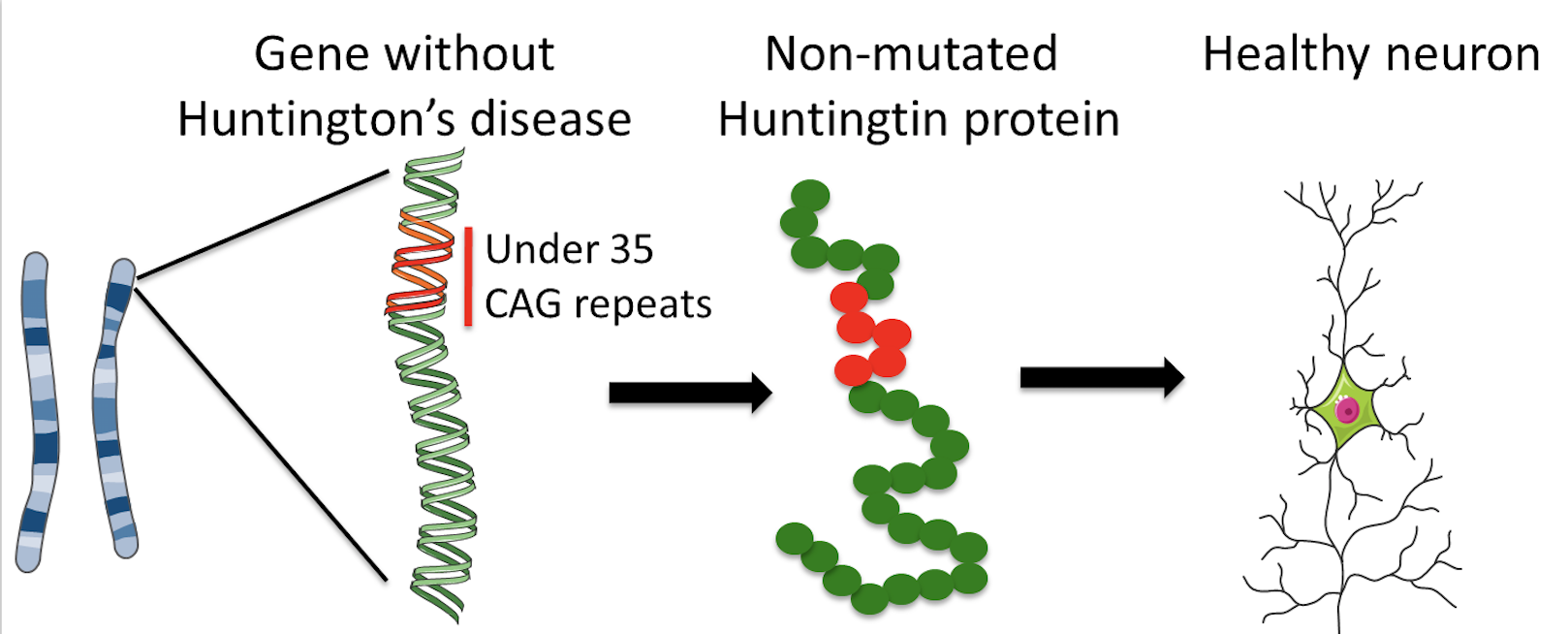
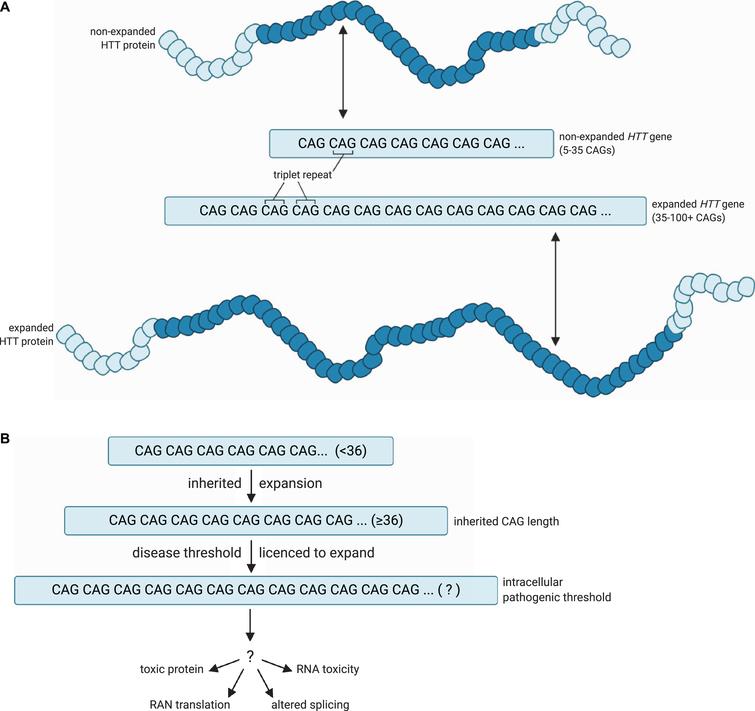
Huntingtons disease HD is caused by a mutated form of the huntingtin gene where excessive more than 36 CAG repeats result in formation of an unstable protein. Each prediction curve spans only the observed age range for data with the corresponding CAG repeat length. CAG repeat expansion in Huntington disease determines age at onset in a fully dominant fashion.
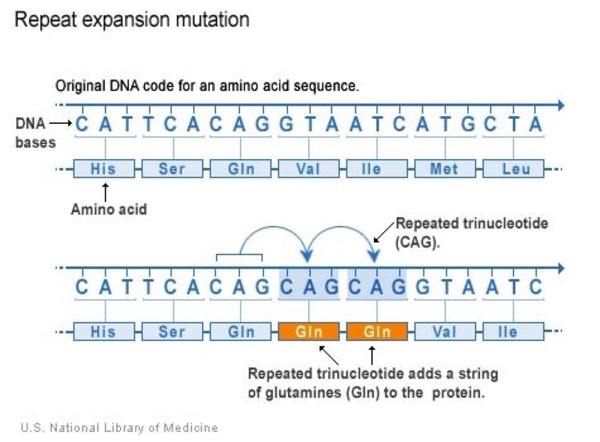
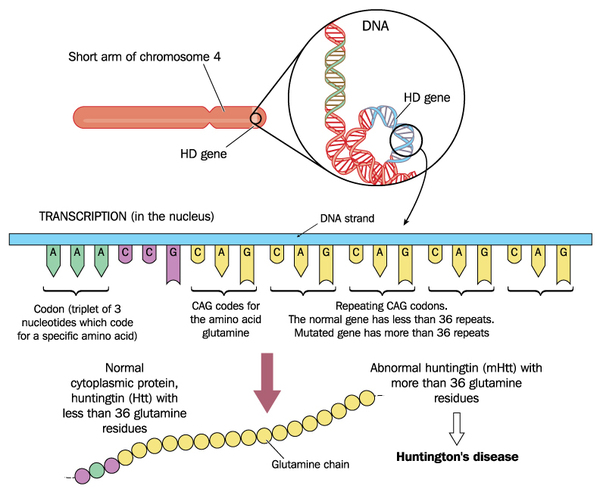
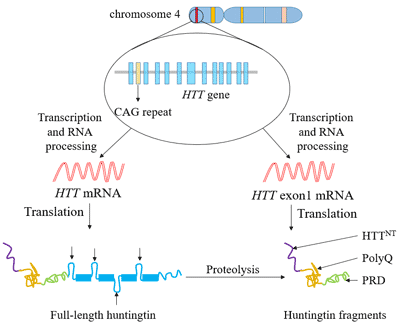
Huntingtons disease is caused by excessive repeats of a portion of DNA called CAG triplets within the HTT gene. Huntingtons disease HD is a genetically determined neurodegenerative disorder identified by the presence of a mutation for a long series of CAG repeats 36 repeats in the Huntingtin HTT gene. The mutation encodes an expanded glutamine tract within the huntingtin protein.
Normal allele CAG length interaction between expanded and normal alleles and presence of a second expanded allele do not influence age at onset of motor manifestations indicating that the rate of HD pathogenesis leading to motor diagnosis is. Huntington disease HD is a neurodegenerative disease caused by CAG repeat expansion in the huntingtin gene HTT and involves a complex web of pathogenic mechanisms. An abnormal number of repeats 36 of cytosineadenineguanine CAG within the huntingtin gene causes the mutation that leads to HD.
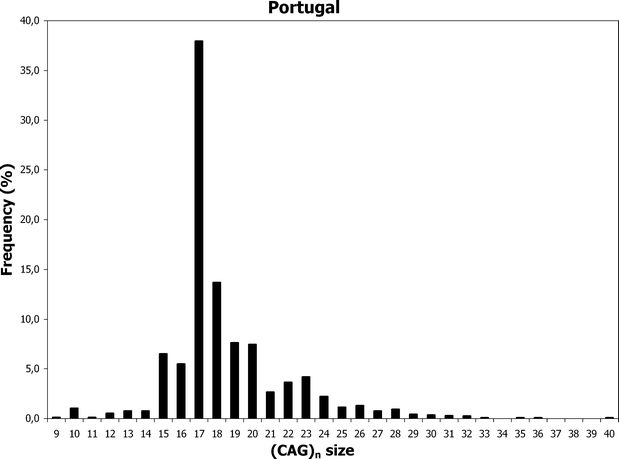
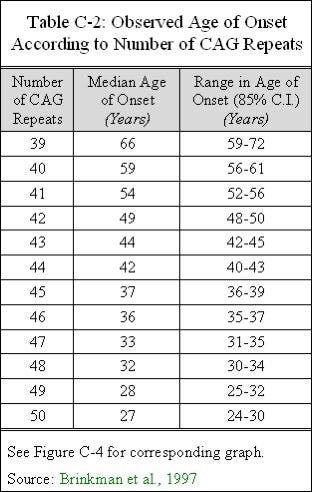
Each CAG triplet carries instructions to produce an amino acid the building blocks of proteins called glutamine. The disease is caused by an expansion of the CAG repeats in 3-5 out of 100000 individuals. A number of statistical models elucidating the relationship between CAG length and AOO have recently been published.
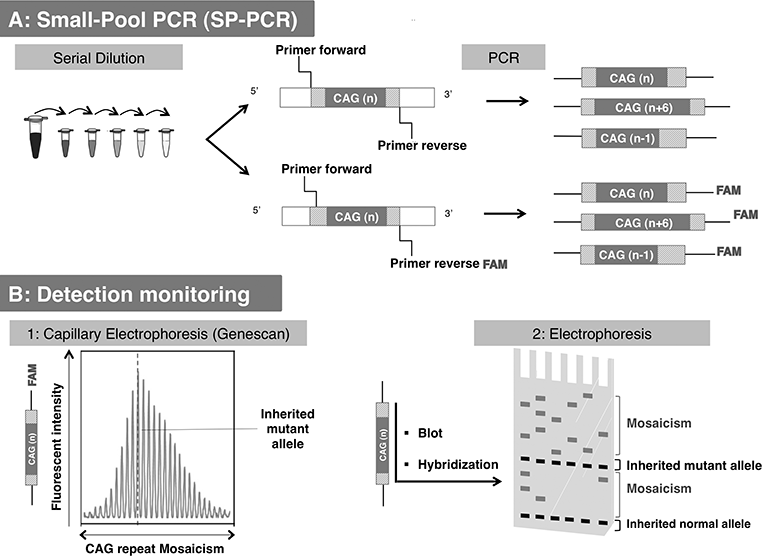
HHT gene CAG repeat expansion GTR Test ID Help Each Test is a specific orderable test from a particular laboratory and is assigned a unique GTR accession number. Transmitting males generally cause the highest expansions in successive generations.
Huntington disease HD is a neurodegenerative disease of mid-life onset that produces choreic movements and cognitive decline often accompanied by psychiatric changes.
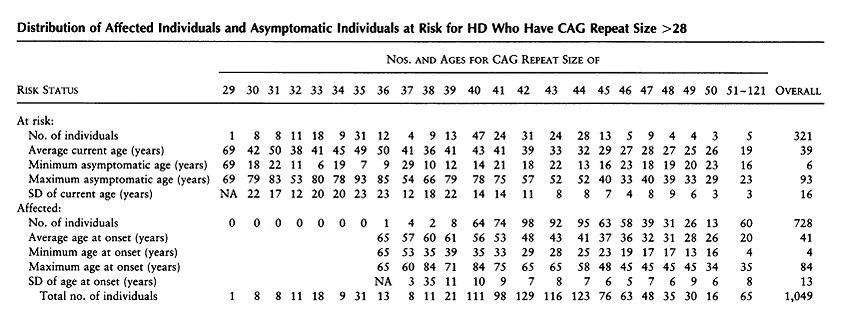
Huntingtons disease HD is an autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disorder that causes cognitive behavioral and motor symptoms. HHT gene CAG repeat expansion GTR Test ID Help Each Test is a specific orderable test from a particular laboratory and is assigned a unique GTR accession number. Huntington disease HD is a neurodegenerative disease of mid-life onset that produces choreic movements and cognitive decline often accompanied by psychiatric changes. CAG-repeat length in the gene for HD is inversely correlated with age of onset AOO. The format is GTR000000011 with a leading prefix GTR followed by 8 digits a period then 1 or more digits representing the version. A-E The CAG repeat length associated with each prediction curve is indicated at the upper right of the curve. Transmitting males generally cause the highest expansions in successive generations. Huntingtons disease HD is an autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disorder that causes cognitive behavioral and motor symptoms. The Huntingtons disease HD mutation influences age at onset through its CAG repeat length a genetic feature that is unstable during intergenerational parent-child transmission.
CAG-repeat length in the gene for HD is inversely correlated with age of onset AOO. The format is GTR000000011 with a leading prefix GTR followed by 8 digits a period then 1 or more digits representing the version. Transmitting males generally cause the highest expansions in successive generations. Huntington disease HD is a neurodegenerative disease of mid-life onset that produces choreic movements and cognitive decline often accompanied by psychiatric changes. Huntington disease HD is a neurodegenerative disease caused by CAG repeat expansion in the huntingtin gene HTT and involves a complex web of pathogenic mechanisms. Each prediction curve spans only the observed age range for data with the corresponding CAG repeat length. CAG repeat expansion in Huntington disease determines age at onset in a fully dominant fashion.
























Post a Comment for "Huntington Disease Cag Repeat"