Death From Celiac Disease
Death from celiac disease. The mean SD age at diagnosis was 322 252 years and 624 were women. While most people with celiac disease experience a relief from symptoms while on a gluten free diet studies are showing an increased mortality rate in patients with the disease compared to. Mainly that she died after a long battle with celiac disease.
1 Cancer Nobody wants cancer and especially nobody wants the type of cancer that can strike people with gut damage. But a few things struck me when I saw this article. Did I know this person.
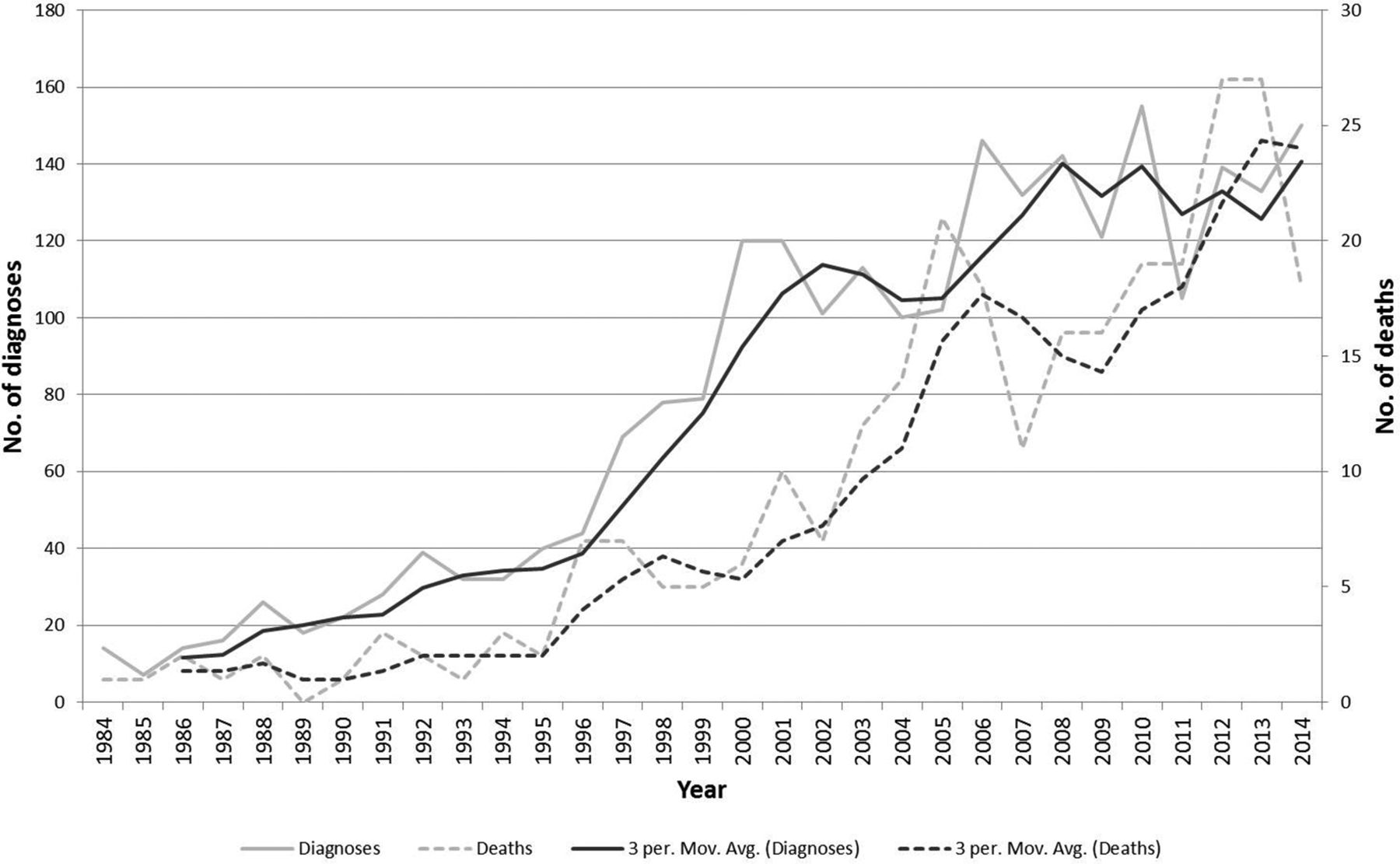
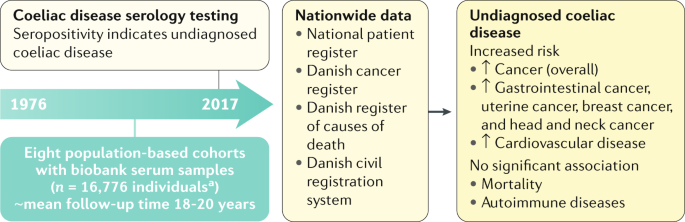
A total of 828 patients with celiac disease died during the follow-up period 1965-1994. There were 49 829 patients with celiac disease including 24 who were diagnosed between the years 2010 and 2017. A higher risk was seen in all causes of death combined.
Among those with celiac disease there were 3049 deaths. Those with Celiac disease villous atrophy had a 280-fold increased risk of death the first year after diagnosis and a 39 increased risk of death over the study period. II show that the observed excess mortality in individuals with CD and LPM was due to a higher proportion of T-NHL in that population.
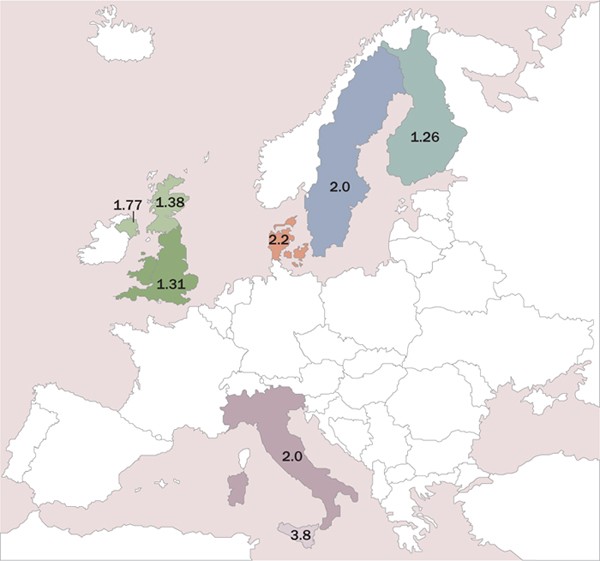
The study included 49829 celiac patients of whom 6596 died during a median follow-up of 125 years. Among the entire population of patients with celiac disease cardiovascular diseases were the leading cause of death in both men and women comprising 394 of all deaths followed by malignant neoplasms as the second leading cause 194 and then digestive diseases 121 and respiratory diseases 98 in both sexes. According to the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences without diagnosis and treatment celiac disease is ultimately fatal.
The increased mortality was greatest within 1 yr of diagnosis of celiac disease and steadily declined over time with the excess mortality being concentrated at ages 45-54 yr in men and 55-64 yr in women. They were compared with nearly 250000 people from the general population. 20-fold 95 confidence interval CI 18-21 among all patients with celiac disease and 14-fold 95 CI 12-16 among patients with celiac disease with no other discharge diagnoses at initial hospitalization.
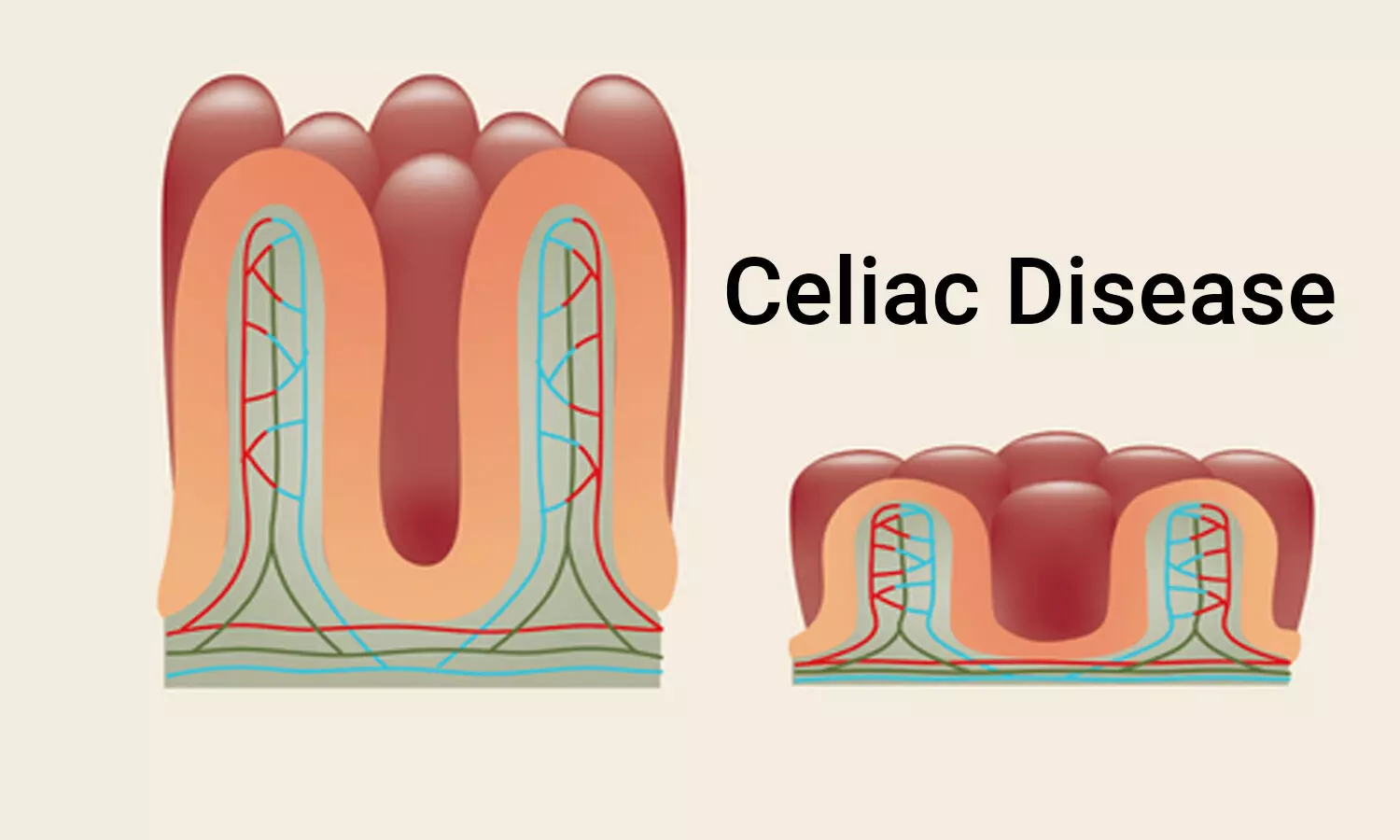
In a person with celiac disease the immune system to gluten responds by attacking the small intestine and inhibiting the absorption of important nutrients into the body. In fact one of the largest cohort studies on Celiac disease patients and mortality published in the Journal of The American Medical Association found that.
Among those with celiac disease there were 3049 deaths.
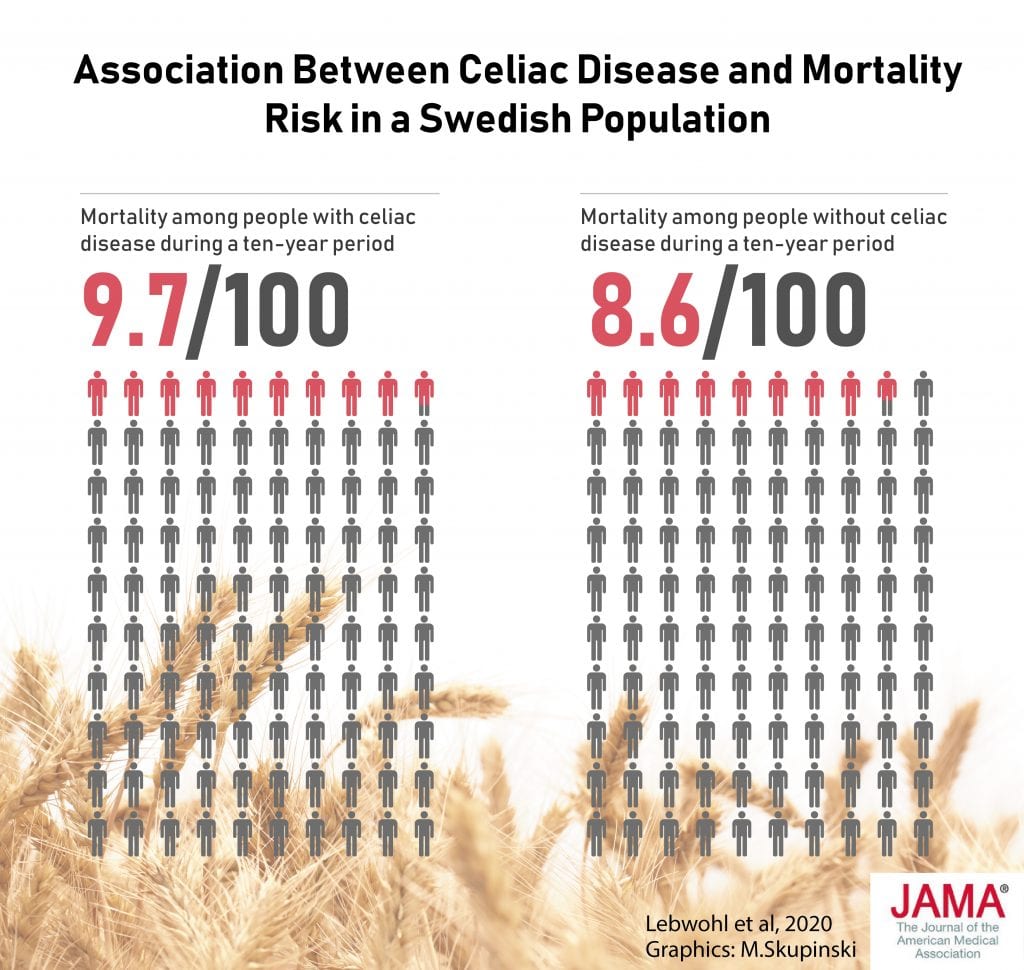
For all causes of death combined mortality risks were significantly elevated. Mainly that she died after a long battle with celiac disease. Those with Celiac disease villous atrophy had a 280-fold increased risk of death the first year after diagnosis and a 39 increased risk of death over the study period. Currently this outcome is rare as most people do well if they avoid gluten. In the vast majority of cases celiac disease is not fatal in the way we normally think of fatal diseasesit wont progress and ultimately kill you. A higher risk was seen in all causes of death combined. Overall people with untreated or unresponsive celiac disease have increased early mortality compared to the general population. They were compared with nearly 250000 people from the general population. They can even lead to death by one of the following.
II show that the observed excess mortality in individuals with CD and LPM was due to a higher proportion of T-NHL in that population. According to the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences without diagnosis and treatment celiac disease is ultimately fatal. In the vast majority of cases celiac disease is not fatal in the way we normally think of fatal diseasesit wont progress and ultimately kill you. While most people with celiac disease experience a relief from symptoms while on a gluten free diet studies are showing an increased mortality rate in patients with the disease compared to. All in all chronic non-responsive or untreated celiac disorder is more likely to cause earlier death of the patient than the general population. II show that the observed excess mortality in individuals with CD and LPM was due to a higher proportion of T-NHL in that population. Currently this outcome is rare as most people do well if they avoid gluten.
/can-celiac-disease-cause-early-death-562338_final-80546f3131654fb0b535030c7c392145.png)



































Post a Comment for "Death From Celiac Disease"